Section 2: Games with Sequential Actions
Key Learning Points
- explain extensive-form games, a finite representation that does not always assume that players act simultaneously.
Activities
- Read Chapter 5 of the textbook.
- Watch the following videos on YouTube:
- Perfect Information Extensive Form: Taste
- Formalizing Perfect Information Extensive Form Games
- Perfect Information Extensive Form: Strategies, Best Response, Nash Equilibrium
- Subgame Perfection
- Backward Induction
- Backward induction, example one
- Backward induction, example two
- Subgame Perfect Application: Ultimatum Bargaining
- Imperfect Information Extensive Form: Poker
- Imperfect Information Extensive Form: Definition, Strategies
- Do the following exercises:
- Consider the perfect-information game in extensive form in Figure 5.2 of the textbook and enumerate the elements of N, A, H, Z, χ, ρ, u of the game according to Definition 5.1.1 (perfect-information game). You may label the choice nodes and terminal nodes.
- Consider the following game, G, with two players, P1 and P2:
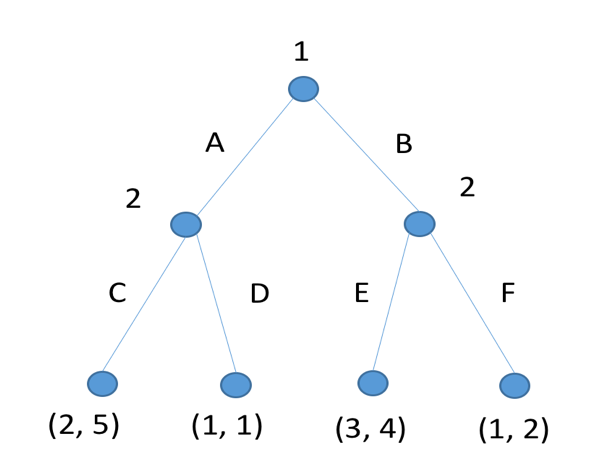
- Use backward induction to compute all subgame-perfect equilibria of this game.
- Describe the normal-form game N(G) that corresponds to G.
- Find all pure Nash equilibria of N(G). Does it have any equilibria that are not subgame-perfect equilibria of G?
Updated June 04 2018 by FST Course Production Staff

